Biopsy Test
1. What is Biopsy?
A biopsy test is a surgical procedure in which a small sample of body tissue or cells is removed to perform further microscopic examination. The typical purpose of this procedure is to aid in the diagnosis or surveillance of a variety of medical disorders, such as cancer, infections, inflammatory illnesses, or other abnormalities.
To reduce pain during a biopsy test, the doctor will typically numb the area or use a local anesthetic. Depending on the location being sampled, numerous types of biopsies are available.
2. Types of Biopsy Test:
Typical biopsy test types include:
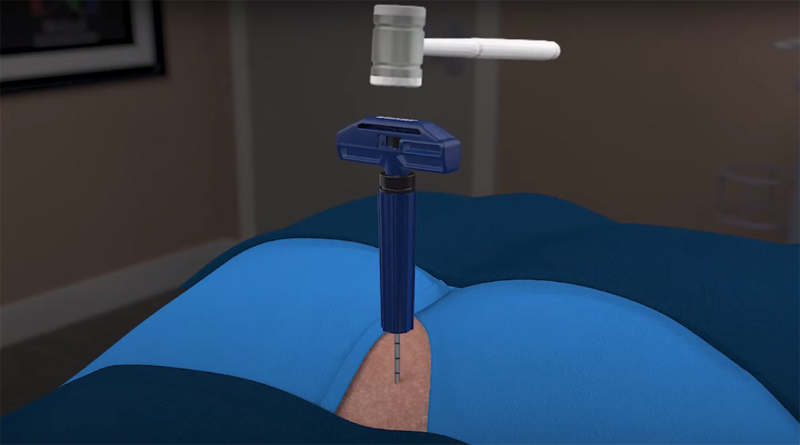
Needle biopsy: Tissue or fluid is removed from the target location using a fine needle. Imaging methods like CT scanning or ultrasound can be used to guide it.
Core needle biopsy: Like a needle biopsy test, this treatment also obtains a larger sample of tissue using a larger needle.
Surgical biopsy: A surgeon will perform this procedure to remove all or a portion of the questionable tissue for testing. Laparoscopy and endoscopy are minimally invasive techniques that can be used, or they can be done through open surgery.
Excisional/Incisional biopsy: In these types of biopsies, the entire lump is removed (excisional) or a portion of it is removed (incisional) for additional examination.
Once the sample has been collected, a pathologist will analyze it under a microscope in a lab setting. They can assess whether the sample contains any aberrant cells or other characteristics that might point to a certain diagnosis.
It is significant to remember that the decision to do a biopsy test depends on the suspected ailment, the location, and the tools that are available. Everybody’s suggested biopsy test procedure is different. To assist you in making an informed choice, your healthcare practitioner will evaluate your medical history, carry out any required exams, and thoroughly describe the operation.
3. Process of a Biopsy Test:
The following steps are commonly included in the biopsy test procedure:
1. Appointment: Your healthcare professional, who is frequently a specialist like a surgeon or a dermatologist, will conduct your initial appointment. Your medical history, present symptoms, and any pertinent imaging or test findings will all be reviewed. They might conduct a physical examination as well.
2. Consent: If a biopsy test is judged necessary, your doctor will go over the procedure’s risks, advantages, and potential drawbacks. You will have the chance to inquire and give your informed approval.
3. Preparation: Your healthcare professional may give you special recommendations to follow before the procedure, depending on the type of biopsy. This may involve avoiding from certain drugs, going without certain foods, or fasting (if necessary).
4. Local anesthesia: To reduce discomfort, a local anesthetic is used to numb the area where the biopsy test will be performed before taking the sample. Usually, an injection or a lotion with a topical anesthetic is used for this.
5. Sample collection: Your healthcare professional will start the biopsy test procedure after the area has become numb. The technique will vary depending on the kind of biopsy that is suggested. For instance:
6. Homeostasis and closure: Any bleeding must be stopped after the sample has been taken, and the wound can then be closed with sutures, staples, or adhesive strips. Dressings that are sterile may be used to cover the region.
7. Sending the sample to the lab: A correctly labeled sample of fluid or tissue is collected and sent to a lab for examination. To make a diagnosis, a pathologist will examine the sample under a microscope and run a number of tests.
8. Results and follow-up: Depending on the complexity of the study, the biopsy test results are normally accessible after a few days or weeks. Your healthcare professional will go over the findings with you, explain the diagnosis, and go through the best course of action, including any additional testing that may be required.
It is crucial to keep in mind that the precise procedure may vary slightly based on the type of biopsy test and the particulars of each example. Based on your unique circumstances, your healthcare practitioner will give you specific instructions and guidance.